Understanding Business Sectors and Environments
Hey! Let’s break down the idea of business sectors and business environments in a way that’s easy to understand and relevant to your everyday life. By the end of this, you’ll see how everything works together in a business, and we’ll throw in some examples that you can relate to — like the apps you use or even your favorite stores!
1. Primary Sector – Getting Raw Materials from Nature
What’s it all about?
This is like the "foundation" of every product you see in the market. It’s all about extracting raw materials from the Earth. Imagine you're at a beach, picking up seashells. That’s similar to what businesses in the Primary Sector do—they collect raw materials from nature.
Examples:
- Mining: Digging for gold, diamonds, or coal. Think of those shiny diamonds in your jewelry — they came from mining!
- Farming: Growing crops like wheat, veggies, or fruits. Ever had a fresh apple? That apple came from farming!
- Fishing: Catching fish to put on your plate for dinner.
- Forestry: Cutting down trees to make paper or furniture.
Why it’s important:
Without this sector, the secondary sector (where stuff gets made) and the tertiary sector (where you buy stuff) wouldn’t exist. We need raw materials like wood, crops, or minerals to create things we use every day.
Example Tip:
Think of this like collecting ingredients for a cake. Without flour, sugar, or eggs, you can’t bake the cake, right?
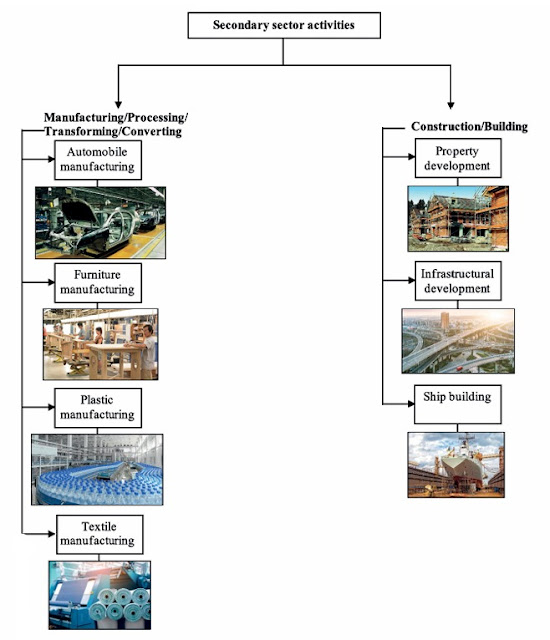
2. Secondary Sector – Turning Raw Stuff into Useful Things
What’s it all about?
Now that you have raw materials from the Primary Sector, it’s time to transform them into something you can use! The Secondary Sector involves turning raw materials into finished products that people need.
Examples:
- Factory Manufacturing: Creating items like clothes, cars, or shoes. The cool sneakers you wear? They came from factories that use raw materials like leather, rubber, and fabric!
- Construction: Building houses, roads, or bridges. Your house? Built with materials like cement, steel, and wood.
- Food Processing: Making things like canned soup or packaged snacks. Your potato chips? They’ve been processed from raw potatoes!
Why it’s important:
This sector adds value to the raw materials from the Primary Sector. Without this transformation, we would just have raw stuff, not products we can use or enjoy.
Example Tip:
It’s like cooking! You start with basic ingredients (primary), then mix them, heat them, and make something new — like a pizza!
3. Tertiary Sector – Services to the Rescue
What’s it all about?
This is the service industry. The Tertiary Sector is about providing services that help deliver finished products to customers. You interact with this sector every day without even realizing it!
Examples:
- Retail: Buying clothes at a store, or ordering food from a restaurant. Ever gone to a mall? That’s a service provided by the retail sector.
- Banking: Keeping your money safe, offering loans, or even giving financial advice. Ever used an ATM? That's the banking sector working.
- Healthcare: Doctors and nurses providing medical help. Your visit to the doctor? A service.
- Entertainment: Watching movies, playing games, or going to a concert. Your Netflix binge? That’s the entertainment sector!
Why it’s important:
This sector is the final link in getting the products to you, the consumer. Without it, all the stuff from the Primary and Secondary Sectors would just sit in warehouses!
Example Tip:
Think of it like the delivery of your food order. After the restaurant cooks it (Secondary Sector), someone has to deliver it to your door (Tertiary Sector) — service to you!
Business Environments – The Outside World That Affects Business
Now, let’s dive into how business environments play a role in how businesses work. Think of environments as different situations in which a business operates. These environments affect how a business runs.
1. Micro Environment – Inside the Business
What’s it about?
This is the inside world of the business. It involves things the business can control, like its own employees, management, and culture.
Examples of challenges:
-
Employees are not motivated: If employees don't want to work, the business won't run well. Imagine you’re working on a group project, and no one wants to participate!
-
Poor working conditions: If the office is too cold or messy, it affects the workers' efficiency. Same goes for a restaurant where the kitchen isn't clean!
Extent of Control:
The business has complete control over its internal environment. It can hire good staff, set policies, and create a positive workplace culture.
Exam Tip:
Remember that Micro = Internal Control! It’s everything inside the business that it can control.
2. Market Environment – The Business World Around You
What’s it about?
This involves everything outside the business that still affects how it operates. These are things the business can’t control directly, but can respond to.
Examples of challenges:
-
Competition: If a new competitor opens a shop nearby with cheaper prices, your favorite coffee shop might lose customers.
-
Changes in customer behavior: If people suddenly prefer tea over coffee, the coffee shop needs to adjust.
-
Supply issues: If a supplier runs out of coffee beans, the coffee shop can’t make your favorite cappuccino!
Extent of Control:
Businesses have some control over this environment. They can adapt, but they can’t fully control it.
Example Tip:
It’s like trying to respond to your friend’s actions. You can’t control what they do, but you can adjust your response!
3. Macro Environment – The Big Picture
What’s it about?
This is everything the business can’t control. These are the big external factors like politics, the economy, or the law that affect every business. These are the uncontrollable factors.
Examples of challenges:
-
Political Changes: The government raises taxes, so businesses have to pay more to operate.
-
Economic Issues: When the economy is in a recession, people spend less money. Your favorite store might lower its prices to attract customers.
-
Environmental Factors: A factory might have to reduce pollution because of new laws. Or think of how businesses are starting to go green due to climate change.
Extent of Control:
The business has no control over these external factors. But it must adapt and respond.
Exam Tip:
Macro = No Control! The business is at the mercy of the outside world. Think of it like weather — you can’t control it, but you have to deal with it!
Activity Example – Naledi Solar Distributors (NSD)
Let’s break this down with an example to make it stick!
NSD Challenges:
-
They can’t pay tax due to financial problems (Internal = Micro).
-
Customers are going to cheaper competitors (Market).
-
The government raises the corporate tax rate (Macro).
Where do these fit?
-
Micro Environment: Financial struggles are a problem NSD can fix by improving management.
-
Market Environment: The business can respond by offering promotions to keep customers.
-
Macro Environment: The government raising taxes is something NSD can’t control — it’s a political change.
Summary – Key Tips for Exams
-
Micro = Inside the business (What you can control).
-
Market = External but close (What you can respond to).
-
Macro = The big outside world (What you can’t control).
Relate each sector and environment to real-life examples like your favorite stores or activities. This will help make things stick!
.png)






.png)
.png)

No comments:
Post a Comment