1. Chromatin
What it is:
- Chromatin is like a spaghetti of very thin thread-like structures inside the nucleus of a cell.
- It's made of DNA and proteins.
- It’s not tightly packed — it looks messy when you see it under a microscope.
Example:
Before a cell divides, chromatin coils up tightly to form chromosomes (those X-shaped structures you often see in diagrams).
Imagine a bowl of spaghetti → that's chromatin.
Twist and pack the spaghetti tightly → that forms chromosomes.
2. Chromatid
What it is:
- When a chromosome copies itself (for example before cell division), each half is called a chromatid.
- So, one chromosome has two chromatids joined at a point called the centromere.
Example:
Think of a pair of shoes:
- Left shoe = 1 chromatid
- Right shoe = 1 chromatid
- Together, they form a full pair (replicated chromosome).
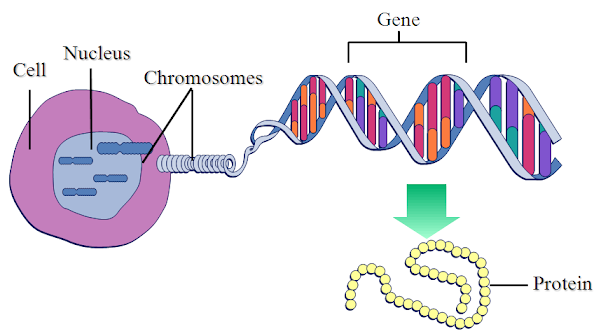
3. Gene
What it is:
- A gene is a small piece of DNA that gives instructions for a specific trait (like eye color, hair type, or blood type).
Example:
- There’s a gene that decides whether you have brown or blue eyes.
- The gene is part of the DNA strand inside your chromosomes.
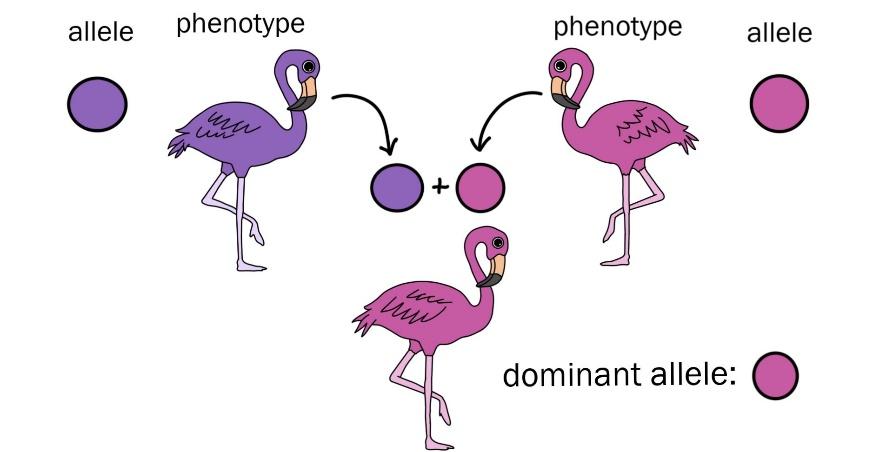
4. Alleles
What it is:
- Alleles are different versions of the same gene.
- They are found at the same position (locus) on a pair of chromosomes.
Example:
For eye color:
- One allele might code for brown eyes.
- Another allele might code for blue eyes.
Now, within alleles, we get:
5. Dominant Allele
What it is:
- A dominant allele shows up in the organism's appearance (phenotype) even if there is only one copy.
Example:
- If "T" = Tall and "t" = Short in plants:
- "Tt" (one Tall allele, one Short allele) → the plant will be Tall because "T" is dominant.
6. Recessive Allele
What it is:
- A recessive allele is hidden when there’s a dominant one present.
- It only shows when there are two copies of it.
Example:
- "tt" (two short alleles) → the plant will be Short.
- "Tt" → the plant will still be Tall because the dominant "T" hides the recessive "t".
7. Phenotype
What it is:
- Phenotype = What you see — the physical traits.
Example:
- Tall plant
- Blue eyes
- Curly hair
Note: The phenotype is determined by the genes (genotype) but also can be influenced by the environment.
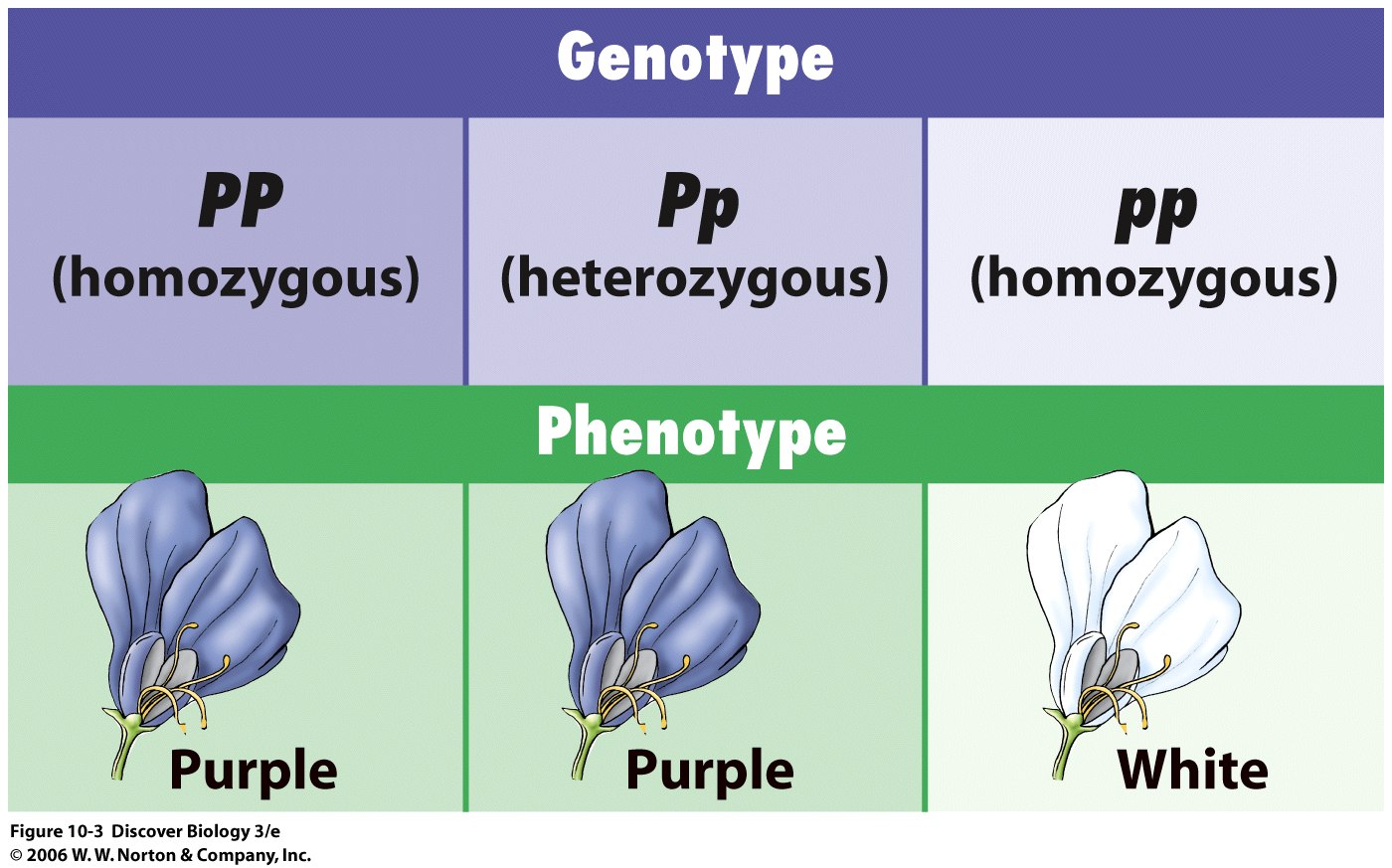
8. Genotype
What it is:
- Genotype = What the genes say — the genetic code inside the cells.
Example:
- TT = two dominant genes for Tall
- Tt = one dominant, one recessive
- tt = two recessive genes for Short
So, Genotype decides Phenotype!
9. Homozygous
What it is:
- Homo = Same
- Two identical alleles for a trait.
Example:
- TT (homozygous dominant — tall)
- tt (homozygous recessive — short)
10. Heterozygous
What it is:
- Hetero = Different
- Two different alleles for a trait.
Example:
- Tt → One Tall (T), one Short (t).
Even though it has a 't', the plant will still be Tall because "T" is dominant.
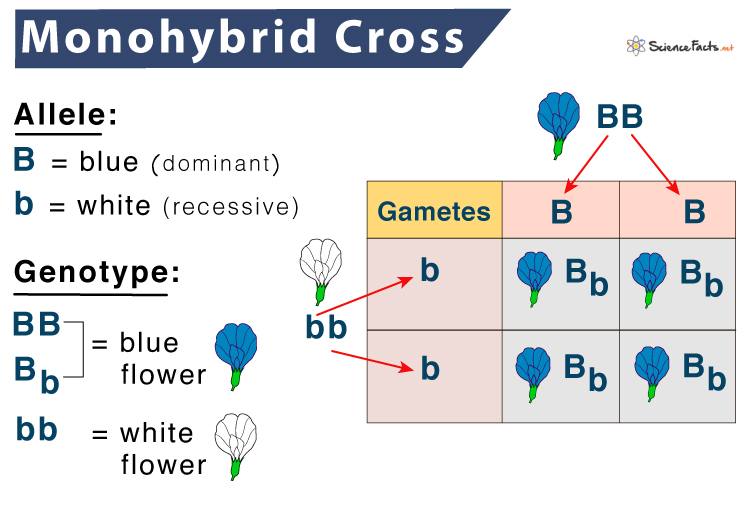
11. Monohybrid Cross
What it is:
- A genetic cross that looks at only one characteristic.
Example:
- Cross between two plants for height only (Tall x Short).
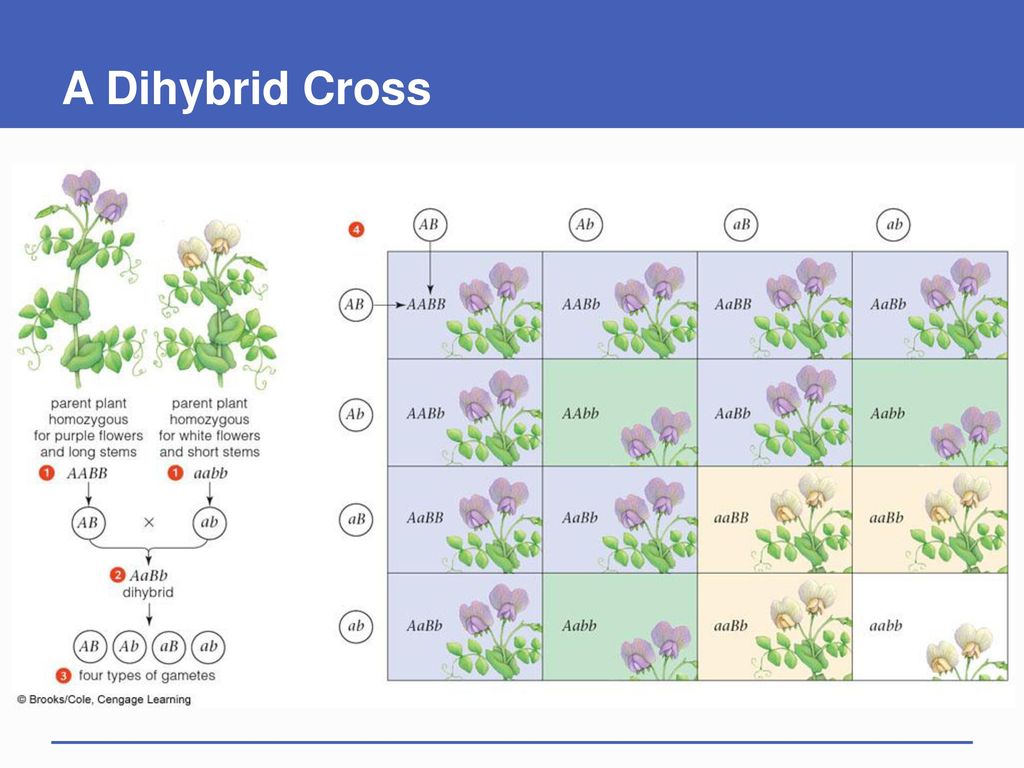
12. Dihybrid Cross
What it is:
- A genetic cross that looks at two characteristics at the same time.
Example:
- Crossing two plants looking at height (Tall or Short) and color (Green or Yellow seeds) together.
13. Karyotype
What it is:
- A picture or map showing all the chromosomes of a cell arranged by size and shape.
- It shows the total number, shape, and arrangement of chromosomes.
Example:
- Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs).
- A karyotype can show if someone has an extra chromosome, like in Down syndrome (an extra chromosome 21).
.png)






.png)
.png)

No comments:
Post a Comment